Energy is the lifeblood of modern society, powering everything from homes and businesses to transportation and industry. As the world faces growing challenges related to climate change, resource depletion, and energy security, the energy sector is undergoing a profound transformation. This blog post explores the key innovations and trends shaping the future of energy, highlighting how advancements in technology and policy are driving a more sustainable and efficient energy landscape.
Transformative Innovations in Energy
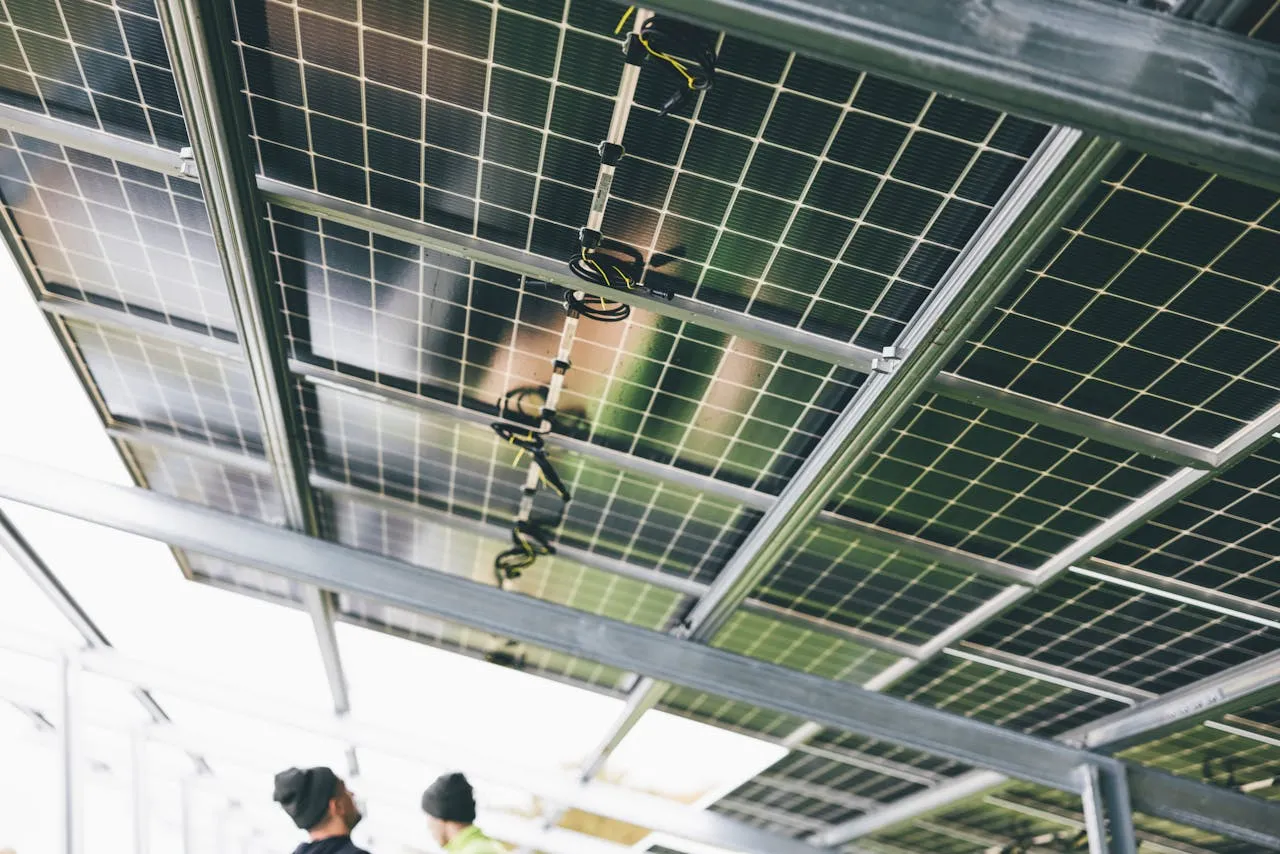
- Renewable Energy Technologies: The shift towards renewable energy sources is one of the most significant developments in the energy sector. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power are becoming increasingly cost-effective and widely adopted. Advances in photovoltaic technology, such as improved solar panel efficiency and energy storage solutions, are making solar power more accessible and reliable. Wind energy is also seeing substantial growth, with larger and more efficient wind turbines being deployed both onshore and offshore. These renewable technologies are crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning away from fossil fuels.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Energy storage plays a critical role in balancing supply and demand, especially with the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources. Innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, are improving energy storage efficiency and capacity. These advancements are enabling better integration of renewable energy into the grid and supporting the development of electric vehicles (EVs). Additionally, large-scale energy storage systems, such as pumped hydro storage and flow batteries, are being implemented to provide grid stability and backup power.
- Smart Grids and Energy Management: The modernization of the electrical grid, known as smart grids, is transforming how energy is distributed and managed. Smart grids use advanced sensors, communication technologies, and data analytics to optimize grid performance, detect and respond to outages, and integrate renewable energy sources. Demand response programs and smart meters allow consumers to manage their energy use more efficiently, contributing to overall energy conservation. These innovations enhance the reliability and resilience of the energy grid while enabling greater participation from renewable energy sources.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: The traditional centralized model of energy generation is being complemented by decentralized systems, such as microgrids and distributed energy resources (DERs). Microgrids are localized networks that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, providing greater energy security and resilience. Distributed energy resources, including rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines, empower individuals and communities to generate their own energy. These systems reduce transmission losses, increase energy independence, and support local energy needs.
- Hydrogen Economy: Hydrogen has emerged as a promising solution for clean energy, particularly in sectors where electrification is challenging. Hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources through electrolysis and used as a fuel for various applications, including transportation, industrial processes, and power generation. Innovations in hydrogen production, storage, and fuel cell technology are advancing the hydrogen economy and supporting its role as a key component of a sustainable energy future.
Impact of Energy Innovations
- Environmental Benefits: The transition to renewable energy sources and the adoption of energy storage solutions contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. By decreasing reliance on fossil fuels, these innovations help lower carbon footprints and improve air quality. The integration of smart grids and energy management systems also supports energy efficiency and conservation, further enhancing environmental benefits.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: The energy sector is a major driver of economic growth and job creation. Investments in renewable energy technologies, energy storage, and smart grid infrastructure create new business opportunities and employment in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. The development of the hydrogen economy also presents potential for economic expansion and innovation in various industries.
- Energy Security and Resilience: Decentralized energy systems and microgrids enhance energy security and resilience by reducing dependence on centralized power sources and improving grid reliability. These systems provide backup power during outages and enable communities to better withstand disruptions. The modernization of the grid with smart technologies also improves the ability to detect and address potential issues, ensuring a more reliable energy supply.
- Consumer Empowerment: Advances in energy technology empower consumers to take control of their energy use and costs. Smart meters and energy management systems allow individuals to monitor and optimize their energy consumption, leading to potential cost savings and greater energy efficiency. The ability to generate and store their own energy also gives consumers more autonomy and flexibility in managing their energy needs.
- Global Impact: The innovations and trends shaping the energy sector have a global impact, influencing energy policies, international trade, and global climate goals. The adoption of clean energy technologies and the commitment to reducing carbon emissions contribute to international efforts to address climate change and promote sustainable development.
Looking Ahead
The future of energy is characterized by continued innovation and transformation. As technology advances and policies evolve, the energy sector will play a crucial role in shaping a sustainable and resilient future. Embracing these innovations and trends will be essential for addressing global challenges, driving economic growth, and ensuring a reliable and clean energy supply for generations to come.
In conclusion, the energy sector is experiencing a revolution driven by advancements in renewable technologies, energy storage, smart grids, and decentralized systems. These innovations are reshaping how we produce, manage, and consume energy, with significant benefits for the environment, economy, and energy security. As we move forward, ongoing research, investment, and collaboration will be key to unlocking the full potential of these technologies and creating a more sustainable energy future.