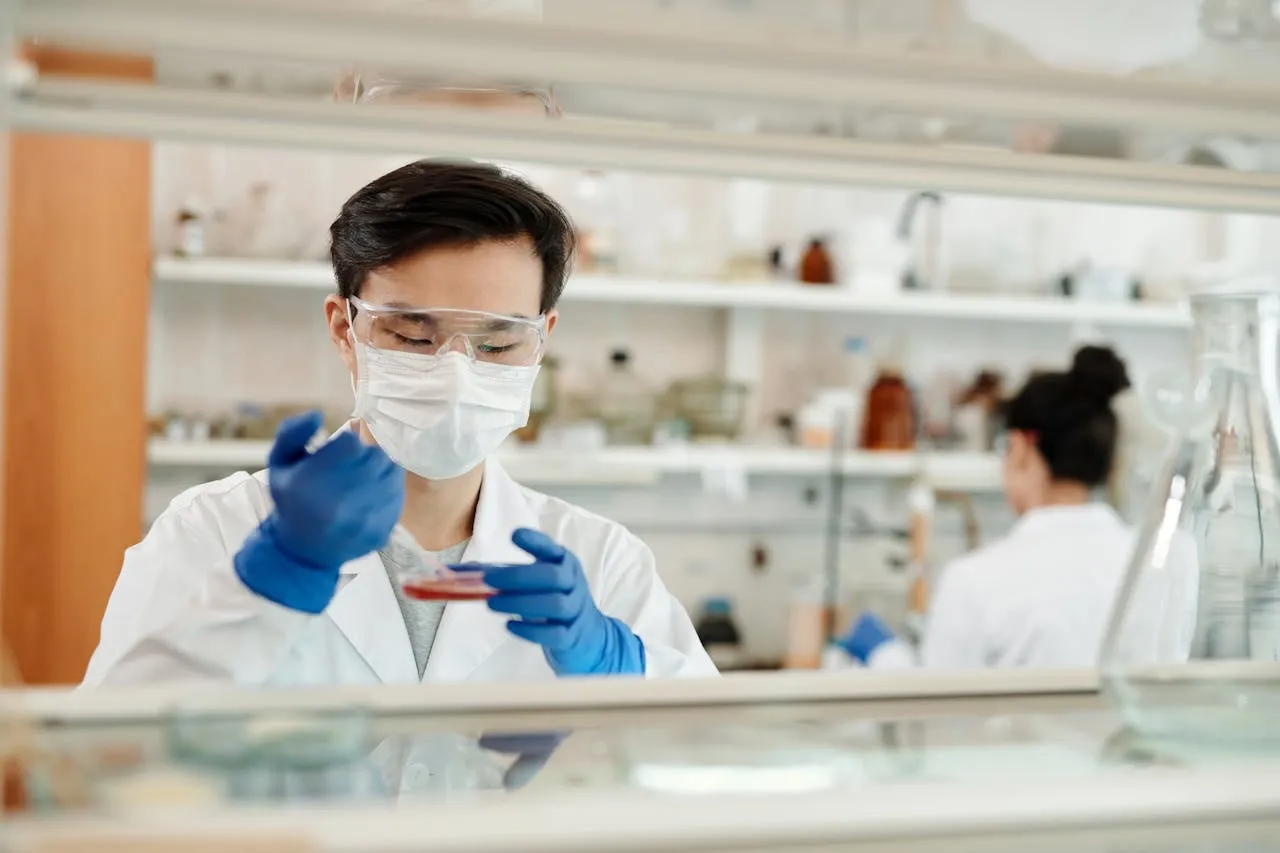
Space stations have become pivotal platforms for conducting scientific research and fostering international collaboration in space exploration. These orbiting laboratories provide a unique environment that enables scientists to conduct experiments and gather data that would be impossible to obtain on Earth. The advancements made aboard space stations not only enhance our understanding of space but also drive innovation in various fields. This article explores the significance of space stations, their contributions to scientific research, and their role in promoting international cooperation.
The International Space Station (ISS): A Symbol of Global Collaboration
The International Space Station (ISS) is one of the most prominent examples of international collaboration in space. Launched in 1998, the ISS is a joint project involving space agencies from the United States (NASA), Russia (Roscosmos), Europe (ESA), Japan (JAXA), and Canada (CSA). It serves as a microgravity laboratory where scientific research can be conducted in an environment free from Earth's gravitational influence.
The ISS orbits Earth approximately every 90 minutes, providing a unique vantage point for observing and studying various phenomena. It supports a wide range of research areas, including biology, astronomy, physics, and materials science. The results of experiments conducted aboard the ISS have led to numerous breakthroughs, such as advancements in drug development, improved materials for use on Earth, and enhanced understanding of fundamental physical processes.
Scientific Research in Microgravity
One of the key advantages of space stations is their ability to provide a microgravity environment, which allows scientists to study physical processes that are otherwise masked by Earth's gravity. Experiments in fluid dynamics, combustion, and materials science conducted in microgravity have revealed new insights that have practical applications both in space and on Earth.
For example, research on the ISS has improved our understanding of how fluids behave in microgravity, leading to advancements in technologies such as water purification systems and combustion engines. Additionally, studies of material growth in space have led to the development of new materials with unique properties, including alloys and semiconductors used in electronics and manufacturing.
Advancements in Space Medicine and Human Physiology
Space stations also play a crucial role in advancing space medicine and understanding the effects of long-duration spaceflight on the human body. The extended stays aboard the ISS provide valuable data on the physiological and psychological impacts of space travel, such as changes in bone density, muscle atrophy, and cardiovascular health.
Research conducted on the ISS helps scientists develop countermeasures to mitigate the negative effects of space travel and ensure the health and well-being of astronauts. This research is critical for preparing for future long-duration missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, where understanding and addressing the challenges of space travel will be essential for mission success.
International Cooperation and Diplomatic Relations
Beyond scientific research, space stations serve as a testament to international cooperation and diplomatic relations. The collaborative nature of the ISS program demonstrates how countries with diverse interests and capabilities can work together towards common goals. The joint efforts in building, operating, and maintaining the ISS highlight the potential for space exploration to foster peaceful collaboration and strengthen international ties.
The ISS has also paved the way for future international projects and partnerships. The experience gained from operating the ISS is being applied to new endeavors, such as the Lunar Gateway, an orbiting space station planned to serve as a staging point for missions to the Moon and Mars.
Future Prospects and Challenges
As we look to the future, space stations will continue to play a vital role in advancing scientific knowledge and fostering international collaboration. Upcoming projects, such as private space stations and new international partnerships, will expand the opportunities for research and exploration.
However, challenges remain, including the need for sustainable funding, technological advancements, and addressing the health and safety of astronauts. Overcoming these challenges will require continued innovation, cooperation, and commitment from the global community.
In conclusion, space stations have become essential platforms for scientific research and international collaboration. Their unique environment allows for groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in various fields, while their collaborative nature exemplifies the potential for peaceful cooperation in space exploration. As we continue to explore the cosmos, space stations will remain at the forefront of scientific discovery and global unity.