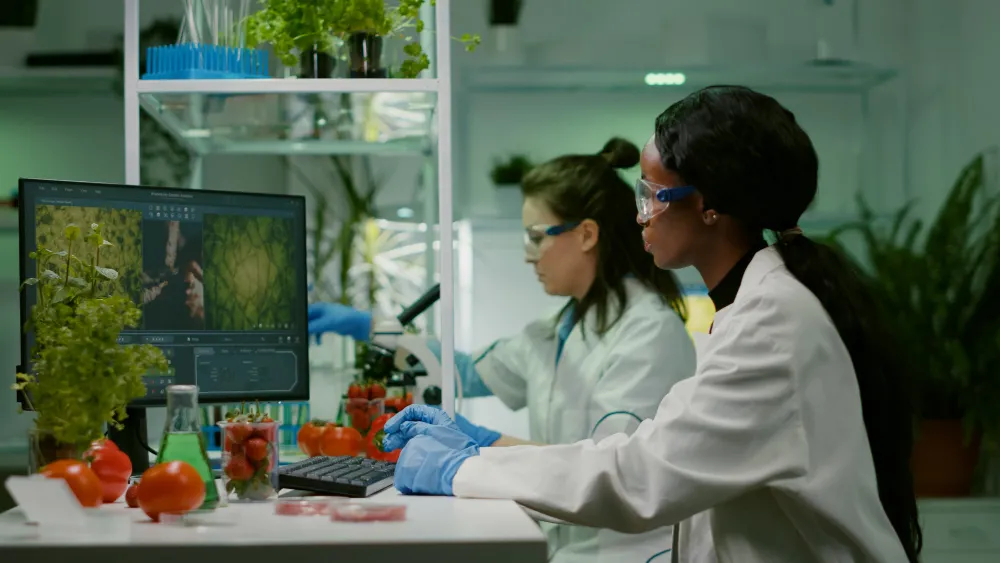
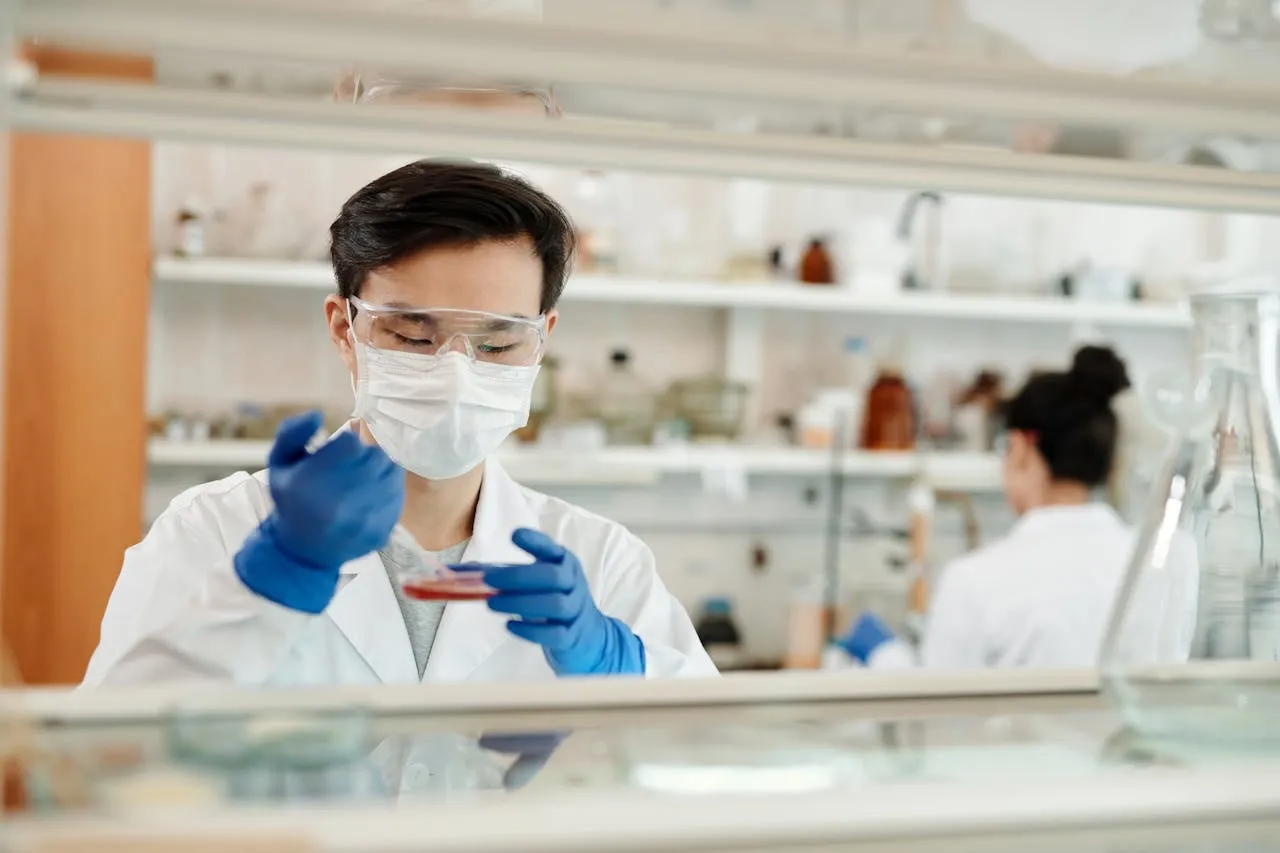
Biotechnology is a field that seamlessly merges the life sciences with cutting-edge technology, paving the way for transformative innovations in medicine, agriculture, and environmental sustainability. By harnessing the power of biological systems, scientists and engineers are developing solutions that not only address some of the most pressing challenges of today but also open up new frontiers for the future. This blog post explores the fundamental concepts of biotechnology, its diverse applications, and the potential it holds for shaping a better world.
The Essence of Biotechnology
Biotechnology refers to the use of living organisms, cells, and biological processes to develop products and technologies that serve human needs. This multidisciplinary field draws from biology, chemistry, genetics, and engineering to manipulate and optimize biological systems for a wide range of purposes. Biotechnology is not a new concept; humans have been using biological processes for thousands of years, such as fermenting beer and bread or selectively breeding plants and animals.
However, modern biotechnology has expanded far beyond these traditional practices. The advent of molecular biology and genetic engineering has enabled scientists to modify organisms at the genetic level, leading to unprecedented advancements in medicine, agriculture, and environmental management. By understanding and altering the genetic code, researchers can create organisms with specific traits, produce life-saving drugs, and develop sustainable alternatives to conventional practices.
Medical Biotechnology: Revolutionizing Healthcare
One of the most impactful areas of biotechnology is in medicine, where it is revolutionizing the way we diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases. Biotechnology has led to the development of a wide range of biopharmaceuticals, including recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies, and vaccines. These biologically derived drugs have transformed the treatment of diseases such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, offering more targeted and effective therapies with fewer side effects than traditional small-molecule drugs.
Gene therapy, a cutting-edge application of medical biotechnology, holds the promise of curing genetic disorders by directly addressing the root cause at the DNA level. By introducing, modifying, or repairing genes within a patient’s cells, gene therapy can potentially cure conditions like cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and certain types of blindness. Recent advancements in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, have made gene therapy more precise, efficient, and accessible, bringing us closer to a future where genetic diseases can be eradicated.
Personalized medicine is another emerging trend in medical biotechnology. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can tailor treatments to the specific needs of each patient, optimizing the effectiveness of therapies and minimizing adverse effects. This approach is particularly valuable in the treatment of complex diseases like cancer, where genetic variations can significantly influence a patient’s response to treatment.
Agricultural Biotechnology: Feeding the World Sustainably
As the global population continues to grow, ensuring food security has become one of the most critical challenges of our time. Agricultural biotechnology offers solutions by enhancing crop yields, improving resistance to pests and diseases, and developing crops that can thrive in challenging environmental conditions. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are at the forefront of this effort, with crops such as Bt cotton, herbicide-resistant soybeans, and drought-tolerant corn providing higher productivity and resilience.
Beyond GMOs, biotechnology is also being used to develop biofortified crops that are enriched with essential nutrients. For example, Golden Rice, which is engineered to contain higher levels of vitamin A, aims to combat vitamin A deficiency, a major cause of blindness and death in children in developing countries. This nutritional enhancement of staple crops can play a crucial role in addressing malnutrition and improving public health.
In addition to improving the traits of crops, biotechnology is promoting more sustainable agricultural practices. Techniques such as tissue culture allow for the rapid multiplication of disease-free plants, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and fertilizers. Biotechnology is also being used to develop biopesticides and biofertilizers that are environmentally friendly and support the health of ecosystems.
Environmental Biotechnology: Sustaining Our Planet
Biotechnology is not only transforming healthcare and agriculture but is also playing a key role in environmental conservation and sustainability. Environmental biotechnology focuses on the use of biological processes to solve environmental problems, such as pollution, waste management, and resource depletion.
One of the most promising applications of environmental biotechnology is in the development of biofuels, which are renewable energy sources derived from biological materials like algae, plant biomass, and waste products. Biofuels offer a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing carbon emissions and dependence on non-renewable resources.
Bioremediation is another critical application, where microorganisms are used to clean up contaminated environments, such as oil spills, heavy metal pollution, and industrial waste sites. These microorganisms break down harmful substances into less toxic forms, helping to restore ecosystems and protect public health.
Biotechnology is also contributing to the development of biodegradable materials, such as bioplastics, which are derived from renewable resources and can be broken down by natural processes. These materials offer a sustainable alternative to conventional plastics, reducing environmental pollution and the impact of plastic waste.
The Future of Biotechnology
As biotechnology continues to evolve, its potential to address global challenges and improve human life is immense. Emerging fields such as synthetic biology, which involves designing and constructing new biological parts and systems, are pushing the boundaries of what is possible. From creating synthetic organisms that produce valuable chemicals to engineering cells that can detect and respond to environmental changes, the future of biotechnology is full of exciting possibilities.
However, with these advancements come ethical and societal considerations. Issues such as genetic privacy, the potential risks of GMOs, and the equitable distribution of biotechnological benefits must be carefully managed. It is crucial to ensure that biotechnology is developed and applied responsibly, with a focus on benefiting society as a whole.
Conclusion
Biotechnology is pioneering the future of medicine, food, and sustainability by harnessing the power of life itself. Whether through the development of life-saving therapies, the creation of more resilient crops, or the promotion of environmental sustainability, biotechnology is shaping a better world for future generations. As we continue to explore the potential of this transformative field, it is essential to navigate the ethical and societal implications to ensure that these advancements benefit all of humanity and the planet we call home.