Space exploration represents one of humanity's most ambitious and transformative undertakings. From the dawn of the space age to the cutting-edge missions of today, our quest to understand the cosmos has driven scientific advancements, technological innovations, and global collaboration. As we continue to push the boundaries of space exploration, the potential to reshape our future and enhance our understanding of the universe grows ever larger.
The Origins of Space Exploration
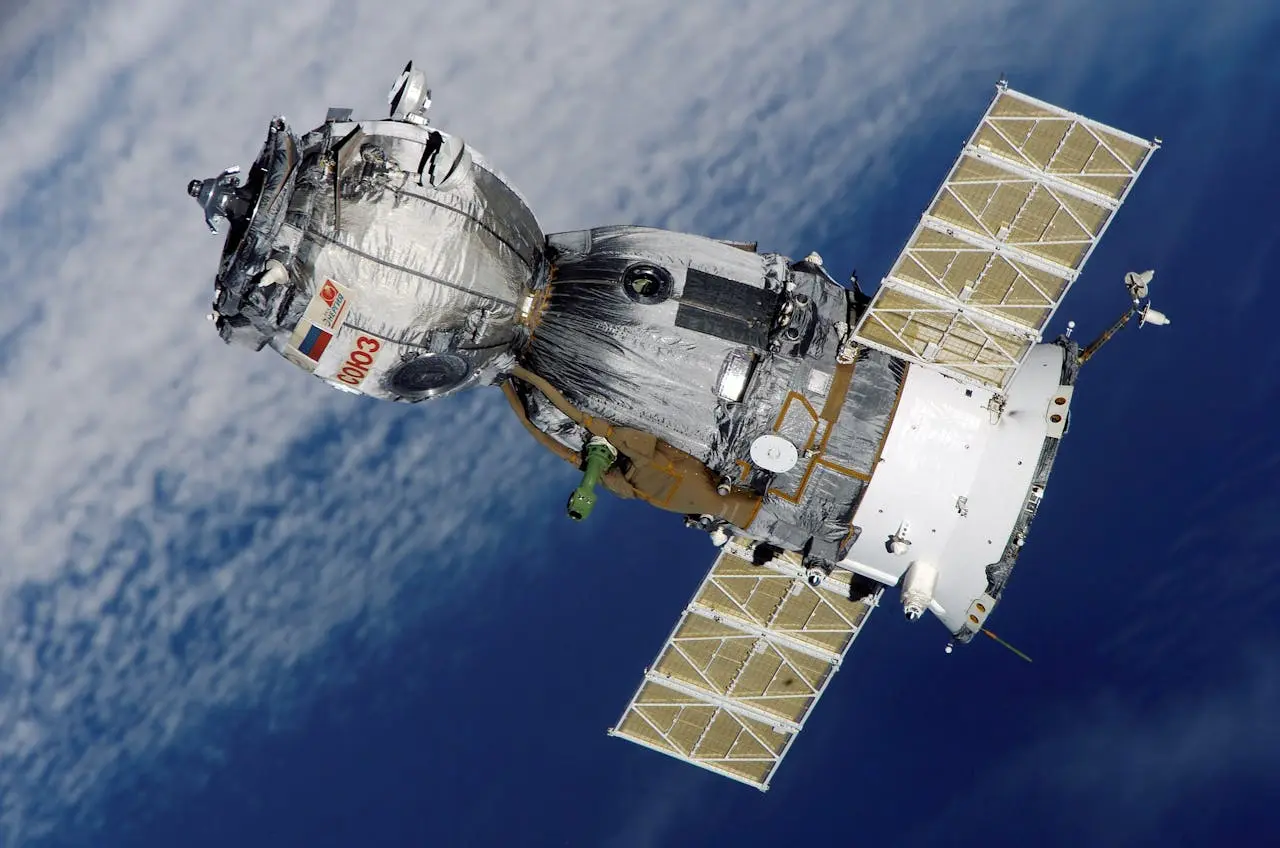
The era of modern space exploration began in the mid-20th century, marked by a series of pivotal achievements. The launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union in 1957 was a landmark event, representing the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth. This achievement initiated the space race and demonstrated that space travel was within humanity's reach.
In 1961, Yuri Gagarin became the first human to orbit Earth, proving that manned space travel was feasible. His flight paved the way for future missions and symbolized the possibility of human exploration beyond our planet. The decade reached its zenith with the Apollo 11 mission in 1969, during which Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed on the Moon, fulfilling the dream of exploring another celestial body and providing a wealth of scientific data about the lunar surface.
Advancements in Space Exploration
In recent decades, space exploration has advanced significantly, driven by both government space agencies and private companies. The International Space Station (ISS), launched in 1998, stands as a testament to international cooperation in space. It serves as a laboratory for scientific research, allowing researchers from around the world to conduct experiments in a unique microgravity environment. The ISS has fostered collaboration between nations and provided valuable insights into the effects of long-term space travel on the human body.
Robotic missions have also played a crucial role in expanding our knowledge of the solar system. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, operational since 1990, has captured breathtaking images of distant galaxies, nebulae, and other cosmic phenomena. These observations have revolutionized our understanding of the universe’s structure, including the discovery of dark energy and the acceleration of the universe's expansion.
Mars exploration has been another focal point of recent missions. Rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance have provided detailed analyses of the Martian surface, searching for signs of past life and assessing the planet's potential for future human colonization. These missions not only enhance our understanding of Mars but also lay the groundwork for potential manned missions to the Red Planet.
The Future of Space Exploration
The future of space exploration is poised to be transformative, with several ambitious projects on the horizon. NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence by the mid-2020s. The program seeks to build infrastructure that will support long-term lunar exploration and serve as a testing ground for technologies needed for deeper space missions, including Mars.
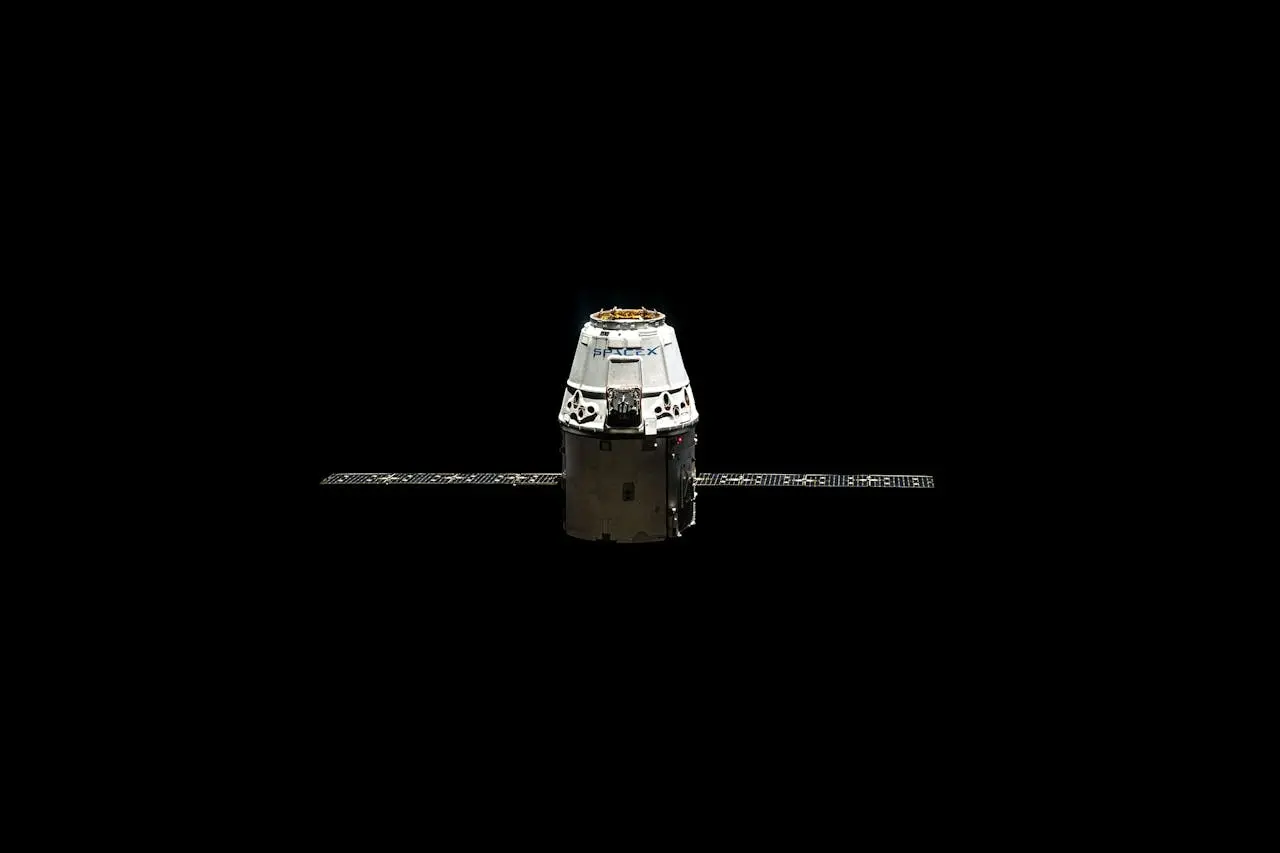
Private companies are also driving innovation in space exploration. SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, has made significant strides with its reusable Falcon rockets and is developing the Starship spacecraft for interplanetary travel. These advancements aim to make space more accessible and affordable, opening the door to new possibilities for exploration and commercial ventures in space.
Asteroid exploration is another exciting frontier. NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission, which successfully collected samples from the asteroid Bennu, highlights the potential for asteroid mining and resource utilization. Such missions could provide valuable resources for future space missions and contribute to our understanding of the early solar system.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, space exploration faces several challenges. The high cost of missions, the harsh environment of space, and the need for advanced technology to ensure astronaut safety are significant hurdles. Additionally, ethical considerations regarding the environmental impact of space activities and the potential for space debris must be addressed.
Conclusion
Space exploration continues to be a source of inspiration and discovery, driving scientific advancements and technological innovation. From the early achievements of Sputnik and Apollo to the sophisticated missions of today, our journey into space has expanded our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it. As we look to the future, the exploration of space promises to reshape our world and inspire future generations to reach for the stars.